Amino acid transporters as a possible effective therapeutic option and drug target in treating of hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common primary liver cancers. The oncogene c-Myc is a transcriptional factor that contributes to malignant transformation. Overexpression of c-Myc in mouse liver can trigger the formation of tumors. However, the molecular mechanism whereby c-Myc exerts its oncogenic activity is still less.
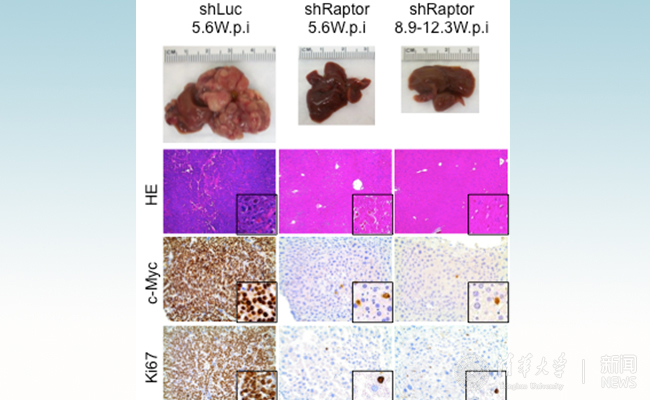
Amino acid transporters play a critical role in the normal function of mTORC1
In a groundbreaking new study jointly by Tsinghua University and UC San Francisco (UCSF), researchers have found that dysfunctional mTORC1 signaling is required for c-Myc driven hepatocarcinogenesis. This article details the process of amino acid transporters in the regulation of oncogene c-Myc induced liver formation and in the activation of the mTORC1 signaling pathway that follows. Activation of the mTORC1 signaling pathway is necessary for c-Myc dependent hepatocarcinogenesis. The downstream of mTORC1 effector eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1 4EBP1 / eIF4E and ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 p70S6K regulate cell proliferation together. Amino acid act as a necessary condition during cell growth and proliferation and plays a key role in the normal functioning of mTORC1. A transcriptome analysis showed that c-Myc can up-regulate the expression of various amino acid transporters, such as SLC1A5 and SLC7A6 (belonging to membrane transporters of the solute carrier (SLC) family). These transporters also have a key role in a variety of physiological and pathological processes. A Metabolomics analysis showed that c-Myc directly up-regulates SLC1A5 and SLC7A6, leading to robust uptake of amino acids and activation of the mTORC1 signaling pathway. In human HCC specimens, there was a significant correlation between the level of c-Myc and the expression of SLC1A5 / SLC7A6. In summary, the data suggests that in addition to the targeting mTOR signaling pathway, the SLC amino acid transporters may be an effective therapeutic option and drug target for the treatment of HCC with activated c-Myc signaling.
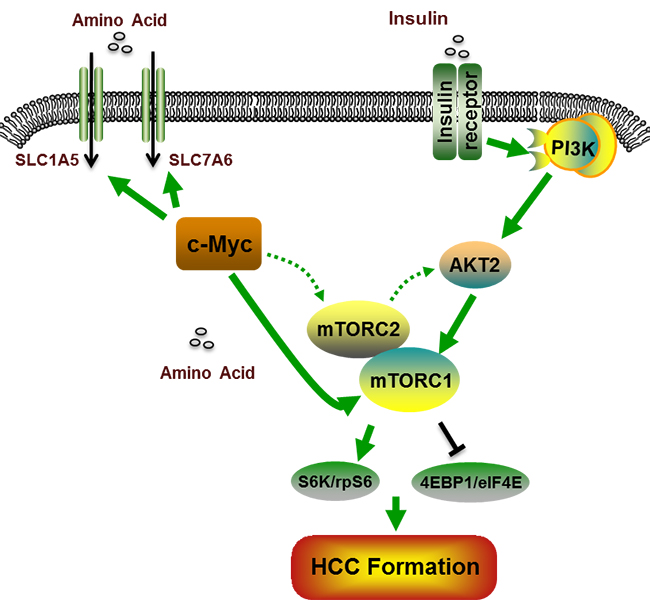
Activation of mTORC1 signaling pathway is the precondition for c-Myc induced hepatocarcinogenesis
The work is published in the journal Hepatology, a world's leading journal in Gastroenterology & Hepatology. The corresponding authors are Prof. Ligong Chen in School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Tsinghua University and Prof. Xin Chen in School of Pharmacy at UCSF. The co-first authors are Mengmeng Ge, a Ph.D. candidate in PTN Graduate program in College of Life Sciences at Tsinghua University, and Pin Liu in UCSF.

